Scope of Project
Problem Statement
The Provider Services Business Unit currently operates with two entities based on the customer profile: physician services and hospital services. These units have many overlapping processes, offerings and can offer greater economies of scale if integrated together. The possible synergy from such integration is the core objective of this project. The impact on the holistic operations of the Unit, the challenges expected and the short/long term activities required to capitalize on this strategic move are part of this project.
Hierarchy of Objectives

This covers the broad areas which can be looked into while analyzing the integration. Suitable strategies can be outlined in these areas which could maximize the benefits. Strategic objectives typically have long term window of impact, Tactical have medium term while Operational have short term window of impact. They also, similarly, have reducing period of time required for the benefits to be visible with Operational objectives having the most immediate effect on efficiency and cost savings.
Project Deliverables
The project deliverables will comprise of a report detailing the methodology followed, the key data points captured, the related analysis and the recommendations for short/long term implementation.
Methodology Followed
Identification of Improvement Areas
Based on preliminary discussions, the primary objectives were categorized into Strategic (Long term value), Tactical (Medium term value) and Operational (Short term value).
On analyzing the processes and interacting with the stakeholders, the viability of pursuing operational process improvements seemed less due to the large diversity in projects, variation in process flows and project level activities and minimal areas for common suggestions in job design and task structures.
Since the core business of the company was in IT BPO Services, the main focus of any recommendations needed to be towards people development and transformation into a learning organization. It was observed that there needs to be greater definition and coherence in communicating the growth opportunities. This implied strengthening the career progression plans and also linking it to a continuous learning program. This would necessitate the development of an aspirational goal framework which would need to factor in linkages with the incentive model and the performance evaluation to ensure that the employees buy-in to the changes in a smooth transition.
Second area which needed to be analyzed was the incentive policy. Due to the presence of only productivity and quality at the lower level and equal distribution among various factors at the higher level, there was less flexibility in the model. Along with this, it did not reflect the job descriptions of the employees, especially at the higher level.
The third area was to do with identification of quantifying parameters to bolster the evaluation of performance on a half-yearly/annual basis. This would bring in more transparency and encourage people to become closer aligned to their main areas of responsibility.
Recommendations
Competency Development
The overall benefits of improvement in Holistic Competency Development and Career Management are greater employee satisfaction, productivity, job knowledge, better talent pipeline, increased motivation.
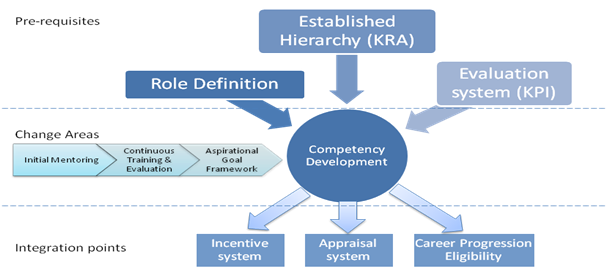
The pre-requisites are necessary because further development of this basic foundation is necessary to make an organization into a learning organization capable of agile change management. The change areas proposed are Initial Mentoring, Continuous Training & Evaluation and Aspirational Goal Framework. These represent the starting point and continuity in an employee’s skill development as well as ties up competency development. The proposals cannot succeed without integration into the current incentive system, the semi/annual appraisal system and the eligibility criteria set for career progression ensuring change adoption.
Initial Mentoring

Continuous Training & Evaluation
Aspirational Goal Framework
Aspirational Goal Framework is a methodology followed by organizations to involve employees in charting their own career path, finding their own interest fields and participating in the learning & career progression process.
Incentive System
The comparison of Incentive System of Hospital Services and Physician Services yields some critical differences.
- At D1, D2 level, the incentive is computed only based on Productivity and Quality. In Physician Services, there are also Collections (Cash targets), Training and Process Improvement.
- The TL, DM, AM level has lower weight for training, process improvement and team in Hospital Services.
- The incentive calculation in Physician Services is proportioned on a prorated basis which is more linear.
- The contribution of the factors to computation of Incentives for TL, DM, AM are Production (75%) and Soft Skills (25%) in Hospital Services while in Physician Services, each factor has an assigned weight
Based on this comparison, the primary areas of suggestion were (1) Introduction of a more balanced incentive system for D1,D2 levels (by inclusion of Training and Process Improvement); (2) Review of weightage contribution for incentives of TL, DM, AM and (3) Financial viability of converting incentive calculation to prorate basis.

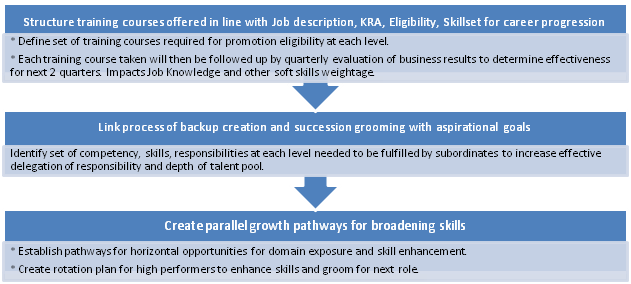
Performance Evaluation

To augment the changes proposed and to move towards becoming a learning oriented organization, the Performance Evaluation Appraisal system needs to mirror a few changes proposed for promoting competency development.
- Quantification of the qualitative factors present in Appraisal form is explored in detail. This is an attempt to explore and identify lines of connection between training, effort and business results.
- The Review of weightage assigned to the various goal heads is an attempt to align appraisal system with incentive system and with the Job Description and KRAs of the designations.
- Integration of Performance Appraisal system with the Training, Evaluation, and Aspirational Goal framework and career progression eligibility has been covered in the previous sections.
The potential benefits of implementing this are that it provides the motivation for employees to adhere to a learning and competency development oriented system. This would promote skill development, align efforts to the job description and responsibilities better and make the process more transparent and measurable.
Implementation – Incentive Model for TL, AM, DM Designations
Of the recommendations given, the first area which was earmarked for immediate implementation was the creation of a new Incentive Model for TL, AM and DM levels of designation. Currently, the 3 designations share a common incentive model which determines their half-yearly incentive eligibility and level of remuneration. The observations suggested that:
1. The current model was clubbing together 3 levels of hierarchy with significant difference in their profiles, job descriptions and role-responsibilities. This was resulting in the incentive model not aligning itself to the actual areas of importance for each designation which would imply rewards for something other than the core responsibility of the employee.
2. The current model had a uniform distribution for all the factors present in the Performance Bucket and similarly equal weightage for the factors present in the Skill set Bucket. This was not aligned to the actual on-ground responsibilities handled by these individuals. The onus on project management, people management, client servicing and more importantly, strategic initiatives needed to be present in the incentive model as well. This would give a clear indication to the individuals of what the organization expects from them and would reward them for contributing to the organization in more than just short-term productivity based areas.
3. The number of factors which were present in the existing model did not accurately reflect the true dynamics and expectations from these individuals. This needed to be re-configured to enhance the focus on core responsibilities through an incentive model which was coordinated with job descriptors as well as performance evaluation criteria.
To address these areas, the Implementation phase focused on building a new incentive model with no bias or correlation in the evaluation of individual factors. Generally, due the inadequacy of a model, managers are forced to make a judgment call while evaluating. This is either due to the absence of defined evaluation parameters which are linked with specific quantified, measurable outputs or due to the limitation of the model in terms of the factors which are present for evaluation. These results in a lot of adjustments required at various levels to ensure that the final rating is aligned to the perceived performance of the individual.
This is what is being targeted for remedy by going through a thorough process of determining an incentive model which is more closely linked with the key performance indicators and key result areas of these designations. For this, the Senior Managers of the Hospital Services Unit were involved end to end due to their role as overall evaluator for each of these designations. The two managers had multiple projects under each of them which differed in their scope, challenges, client deliverables, work processes etc. To ensure the model is uniform, the managers were asked to collaborate from the first stage itself to come up with a model which would address the common areas which would take care of project variability in the present as well as future. Their involvement also ensures that the methodology followed is shared with the company for future reference and use.
Methodology
The New Incentive Model would be derived by following the steps given below:

Conclusion
In conclusion, we can say that the incentive model which would be determined by following this mathematical process would ultimately completely depend on the quality of data input into the model. If there are discrepancies here, the model itself would be faulty. Finally, the weightage suggested by the model are a mathematically derived guideline which could be used for reference while designing the weightage as well as the new incentive model. The entire exercise itself would serve as a great learning in embarking on this strategic move.
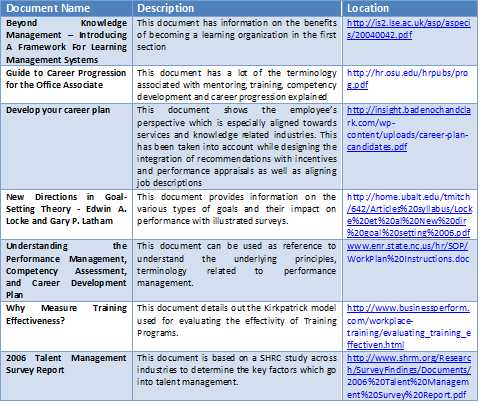
Recommended Supplementary Readings

Nabarun Sengupta
Masters Of Business Administration (2010-2012)
IIT Kanpur



Thu, Sep 1, 2011
In Focus