Mobile and Wireless Communication systems will allow 5G support for the expected increase in data volumes and broadening in the range of application domains. 5G systems are built upon the evolution of existing technologies complemented by new radio concepts that are designed to meet the new and challenging requirements shown in Figure 1. Essential services such as e-banking, e-learning and e-health will continue to proliferate and become handier for pocket devices. Evolutionary research has been carried out on the development of interactive television (iTV), Video on Demand (VoD) and broad wireless internet contents, which will progressively be delivered over mobile and wireless systems. These developments will lead to an avalanche of mobile and wireless traffic volume, projected to increase a thousand-fold over the next decade. Furthermore, some applications will impose additional and very diverse requirements on mobile and wireless communication systems that 5G will have to support.
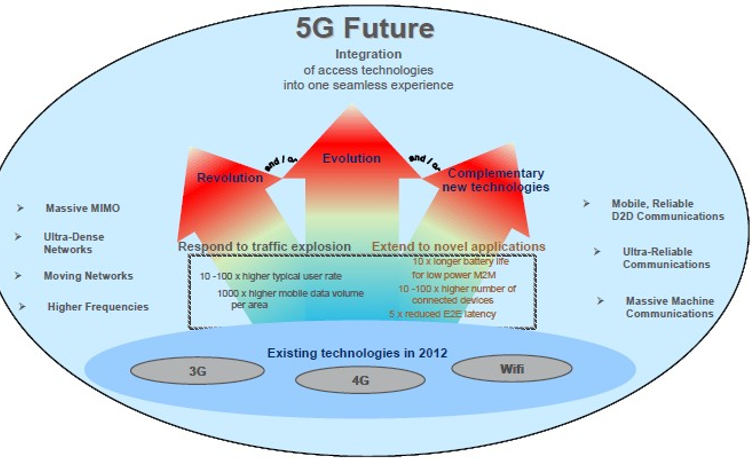
Figure 1: Evolution and New technologies of 5G (Originated from METIS project document)
Four generations of cellular communication systems have been adopted in the USA with each new mobile system generation emerging every 10 years or so since the 1980s: first generation analog FM cellular systems in 1981; second generation digital technology in 1992, 3G in 2001, and 4G LTE-A. The evolution from 1G to 5G is summarized in Table 1. Existing base station designs must service different bands with different cell sites, where each site has multiple base stations (one for each frequency or technology usage e.g. third generation (3G), fourth generation (4G), and Long Term Evolution-Advanced (LTE-A). To procure new spectrum, it can take a decade of legal formalities through the regulatory bodies such as International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC). When spectrum is finally licensed, incumbent users must be moved off the spectrum, causing further delays and increasing costs.
| Generation | Requirements | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| 1G | No official Requirements. Analog Technology | Deployed in 1980s |
| 2G | No official requirements. Digital Technology | First digital Systems. Deployed on 1990s. New services such as SMS and low rate data |
| 3G | ITU’s IMT-2000 required 144 kbps mobile, 384 kbps pedestrian, 2 Mbps indoors | Primary technologies include CDMA 2000 1X/EV-DO and UMTS-HSPA. WiMAX now an official 3G technology |
| 4G | ITU’s IMT-Advanced requirements include ability to operate in up to 40MHz radio channels and with very high spectral efficiency | No technology meets requirements today. IEEE 802.16m and LTE-Advanced being designed to meet requirements |
| 5G | IMT-A supporting for heterogeneous wireless devices added to IP architecture of 4G communication system | 10Gbps peak data rates with 8~10bps/Hz/cell. New system concepts to boost for this wireless network |
Challenges and Prospects of 5G Wireless Technology
With the IMT-Advanced (IMT-A) standards ratified by the International Telecommunications Union in November 2010 and IMT-A, i.e., the fourth generation (4G), wireless communication systems being deployed in the world, the fifth generation (5G) mobile and wireless communication technologies are emerging into research fields. Based on the Internet Protocol Architecture of 4G communication systems, unprecedented numbers of smart and heterogeneous wireless devices will be accessing future 5G mobile and wireless communication systems with a continuing growth of Internet traffic. Therefore, compared to 4G communication systems, significantly higher wireless transmission rates are expected in 5G communication systems, such as 10 Gbps peak data rates with 8~10 bps/Hz/cell. Moreover, energy efficient concepts will be fully integrated into future wireless communication systems to protect the environment. To meet the above challenges, 5G mobile and wireless communication systems will require a mix of new system concepts to boost spectral efficiency, energy efficiency and the network design, such as massive MIMO technologies, green communications, cooperative communications and heterogeneous wireless networks. We expect to explore the prospects and challenges of 5G mobile and wireless communication systems combining all of the above new designs and technologies. Thus concluding, simultaneous management of multiple technologies in the same band limited spectrum is a challenge in 5G mobile communication which supports going beyond voice for newer smart phones and advanced mobile devices. Gathered data for meeting the requirements and satisfactory constraints are highly valuable for the development of 5G cellular communications at mm bands in the coming decade.

 © Nerd Magazine, IIT Kanpur,2017. All rights reserved.
© Nerd Magazine, IIT Kanpur,2017. All rights reserved.
Comments
comments powered by Disqus