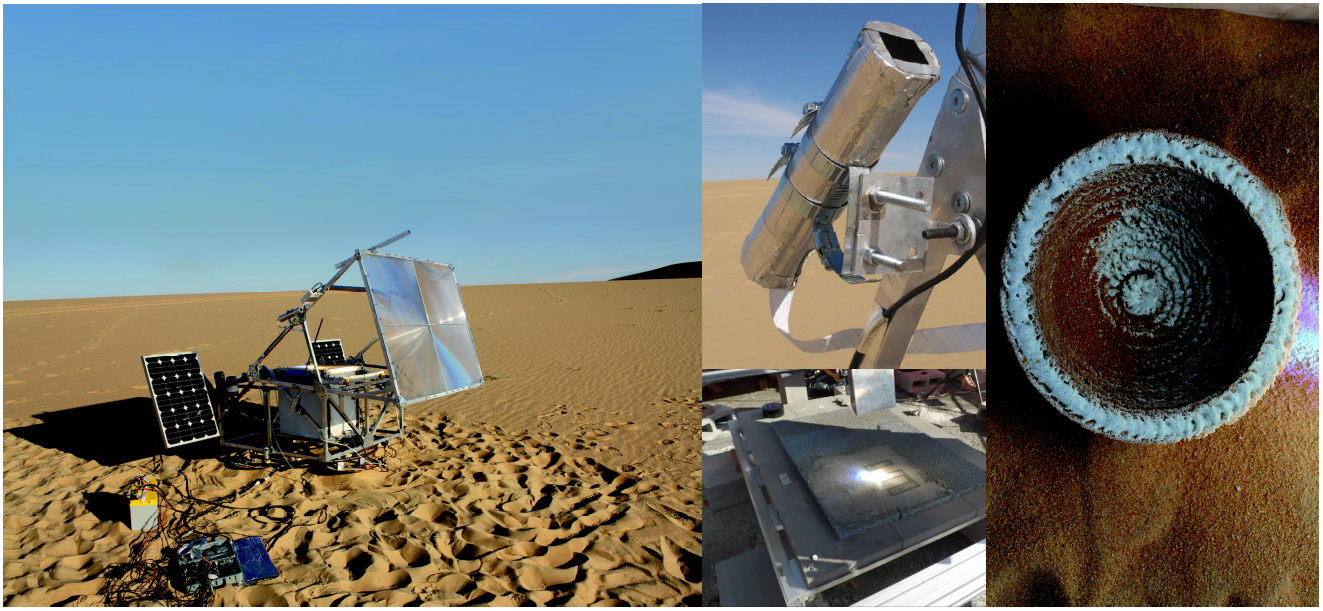
 Proposed Activity 1:
Proposed Activity 1: In-situ lunar manufacturing.
We are currently developing technology to demonstrate automated in-situ manufacturing on the Moon. In-situ manufacturing utilizes only locally available resources. Thus, on the moon the working material will be lunar regolith, and only solar power will be used. Challenges are, of course, immense, including
- researching the right manufacturing strategy for lunar regolith;
- harnessing solar energy to enable necessary heating and to provide power;
- automation of the entire process; and
- making the equipment portable, and space qualified.
Scientific and social impact:
- In-situ manufacturing will greatly enhance space exploration. Lunar surface is unable to provide resources to accomplish manufacturing through usual methods – at present these resources are transported from Earth, which increases the mission cost and/or diminishes the mission’s goals.
- This will be a stepping stone towards the creation of waypoints / transportation hubs that extend the lifetime of a mission and, even, lunar habitation.
- At the same time, there will be positive social impact. The ability to manufacture goods in situ (locally) will enable manufacturing in remote and/or resource deprived regions of India. Furthermore, local manufacturing will reduce the carbon footprint, making it more sustainable.
Requirement: We need to rapidly hire the best available project engineers and develop space qualified testbeds, laboratories and workshops.
Proposed Activity 2: Detection and Characterization of Exoplanets using CubeSats.
Today, more than 5500 exoplanets are confirmed, and multiple surveys are ongoing and planned to discover more that pushes our understanding of planet formation and their evolution processes. The field is moving towards characterization of these known planets.
Scientific importance:
- Critical to humanity’s search for habitability in outers space, answers to planet formation, and astrobiology.
- Big science at small cost. With recent advancements in CubeSat technology - miniaturized sensors and instruments — cutting edge research can be achieved in a cost-effective manner.
Social impact:
- Outreach. CubeSat projects frequently involve students and early-career researchers, providing valuable hands-on experience in designing, building, and operating space missions. These projects foster skill development and inspire the next generation of scientists, engineers, and innovators.
- Affordable Access to Space Science. CubeSats offer a cost-effective platform for exoplanet detection and characterization. The use of CubeSats for discovering and studying exoplanets captures public imagination, sparking interest in the search for life beyond Earth and advancing our understanding of the cosmos. These missions will generate excitement about humanity’s place in the universe.
 Proposed Activity 3:
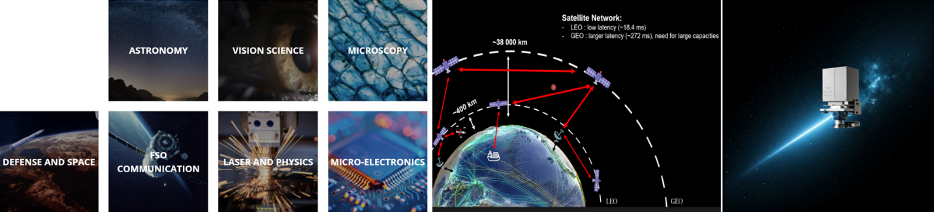
Proposed Activity 3: Adaptive Optics Lab for Ground to Satellite Optical Communication
Adaptive optics (AO) is a versatile technology that has transformed the field of optics by correcting aberrations in optical systems in real-time. It was initially developed for astronomical purposes, but has since been applied in various fields such as microscopy, ophthalmology, optical and quantum communication, defense, and remote sensing.
The Adaptive Optics Lab will play a critical role in advancing ground-to-satellite optical communication by mitigating the effects of atmospheric turbulence on signal quality. This capability is vital for achieving high-speed, reliable data transfer between ground stations and satellites, supporting applications such as broadband internet, Earth observation, and space exploration.
Scientific and social impact:
- Global Connectivity. Adaptive optics improves satellite internet infrastructure, providing fast and reliable internet access, especially to remote and underserved areas.
- Education and Workforce Development. The lab serves as a hub for training the next generation of scientists and engineers, promoting technological growth and innovation.
- Economic Growth. By improving communication technology, it supports industries like telecommunication, space exploration, and defense, contributing to economic progress.
 Proposed Activity 1: In-situ lunar manufacturing.
Proposed Activity 1: In-situ lunar manufacturing. Proposed Activity 3: Adaptive Optics Lab for Ground to Satellite Optical Communication
Adaptive optics (AO) is a versatile technology that has transformed the field of optics by correcting aberrations in optical systems in real-time. It was initially developed for astronomical purposes, but has since been applied in various fields such as microscopy, ophthalmology, optical and quantum communication, defense, and remote sensing.
Proposed Activity 3: Adaptive Optics Lab for Ground to Satellite Optical Communication
Adaptive optics (AO) is a versatile technology that has transformed the field of optics by correcting aberrations in optical systems in real-time. It was initially developed for astronomical purposes, but has since been applied in various fields such as microscopy, ophthalmology, optical and quantum communication, defense, and remote sensing.