- Applied Data Science & Machine Intelligence: Fundamentals to Next Generation AI: 1st June to 15th July 2026 New
- Admissions 2025-26 Semester-II Announcements New
- IIT Kanpur Certificate Program on Python QISKIT for Data Science, Data Analytics, Machine Learning (ML) and Quantum Computing, 1st March to 27th March 2026 New
- Notice for Spot PhD Admissions
- The IEEE DEIS Summer School 2025 on the theme of 'Insulating and Multifunctional Dielectrics' was hosted for the first time in India, at IIT Kanpur, from 20th to 25th September.
- IIT KANPUR Certificate Program on PYTHON + MATLAB/ OCTAVE-Based Simulation and Design of 5G/ 6G Wireless Technologies, 1st September to 26th September 2025
- Dr. Meena Mishra, DRDO graced us as the Guest of Honour for the 58th Convocation.
- Farewell to the class of 2025 organized by EEA on 22nd April 2025
- Workshop on "Metamaterial Antennas and Applications" was successfully conducted from April 18-20 2025, coordinated by Prof. Raghvendra Kumar Chaudhary and Prof. Kumar Vaibhav Srivastava
- Invited Lecture by Prof. Akhilesh Jaiswal (University of Wisconsin-Madison, USA) titled "Unconventional Computing Paradigms from Extreme-Edge to Extreme-Scale" was successfully conducted on 15th April 2025
- EMI/EMC (Electromagnetic Interference and Compatibility) and Electrical Safety Test Facility, accredited by National Accreditation for Testing and Calibration Laboratories (NABL) was launched on 5 April, 2025 at IIT Kanpur under the leadership of Prof. M. Jaleel Akhtar
- Happy Hours for UG students organized by EEA on 24th March 2025
- Invited Lecture by Prof. Souvik Mahapatra (IIT Bombay) titled “A Device (TCAD) to Circuit (SPICE) Framework for BTI and HCD Aging” was successfully conducted on 24th February 2025
- Lecture by Prof. Saurabh Lodha (IIT Bombay) titled “Engineering the strain and neuromorphic performance of 2D-TMD transistors” was successfully conducted on 25th February 2025
- Invited Lecture by Mr. Milind Dhighrasker, Senior Director, ON Semiconductors titled “Overview of Design Challenges for SiC-based Traction Inverters” on 31st January 2025
- Invited Lecture by Prof. William G. Whittow, Wolfson School of Mechanical, Electrical and Manufacturing Engineering (WSMEME) at Loughborough University titled “Recent Advances in Reconfigurable RF Frontend Systems” was successfully conducted on 6th January 2025
- Bonfire Evening - Relive the Joys of College Days organized by EEA on 4th January 2025
- Invited Lecture by Prof. Srabanti Chowdhury (Stanford university) titled “Unleashing the Potential of Wideband Gap Materials” was successfully conducted on 2nd January 2025
Admissions 2025-26 Semester-II Announcements Read More...
Notice for Spot PhD Admissions Read More...
Addendum: The additional list of the provisionally shortlisted candidates for MTech interview for Part-Time/External/Sponsored position can be found Read More...
 Welcome to the Department of Electrical Engineering (EE) at IIT Kanpur. The EE department is one of the oldest departments at IIT Kanpur. It was one of the first five departments with which IIT Kanpur started in 1960. Subsequently, the Advanced Centre for Electronics Systems (ACES) came into existence in early 1970 by a grant from the Ministry of Defence to undertake manpower training and to carry out research and development related to defense. Subsequently, several sponsored projects in many subject areas with large interdisciplinary content were handled through ACES. ACES is now an integral part of the EE department and houses the majority of EE laboratories and facilities. The department is currently the largest multidisciplinary department at IIT Kanpur. It covers practically all sub-disciplines in Electrical and Communication Engineering including Power Systems, Power Electronics, Microwaves, RF techniques, Microelectronics, VLSI, Photonics, Control Systems, Robotics, Speech, and Audio Processing, Computer Vision, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Wireless Communication, Computer Networks, Future wireless networks like 5G/6G, Wireless sensor networks, and IoT networks. Read more
Welcome to the Department of Electrical Engineering (EE) at IIT Kanpur. The EE department is one of the oldest departments at IIT Kanpur. It was one of the first five departments with which IIT Kanpur started in 1960. Subsequently, the Advanced Centre for Electronics Systems (ACES) came into existence in early 1970 by a grant from the Ministry of Defence to undertake manpower training and to carry out research and development related to defense. Subsequently, several sponsored projects in many subject areas with large interdisciplinary content were handled through ACES. ACES is now an integral part of the EE department and houses the majority of EE laboratories and facilities. The department is currently the largest multidisciplinary department at IIT Kanpur. It covers practically all sub-disciplines in Electrical and Communication Engineering including Power Systems, Power Electronics, Microwaves, RF techniques, Microelectronics, VLSI, Photonics, Control Systems, Robotics, Speech, and Audio Processing, Computer Vision, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Wireless Communication, Computer Networks, Future wireless networks like 5G/6G, Wireless sensor networks, and IoT networks. Read more
 Welcome to the new Optoelectronics and Optical Communication stream in the Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Kanpur. The stream offers M.Tech and PhD programs imparting excellent training in areas ranging from semiconductor optoelectronics to optical networks.
Welcome to the new Optoelectronics and Optical Communication stream in the Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Kanpur. The stream offers M.Tech and PhD programs imparting excellent training in areas ranging from semiconductor optoelectronics to optical networks.
Faculty
PG Students
Publications
Facilities
Courses
- Details
- Last Updated: Monday, 03 March 2025 15:11
Welcome to the Controls and Automation group in the Department of Electrical Engineering, IIT Kanpur. The stream offers M.Tech. and PhD programs.
 On the control systems front, the research interests of the group include applications of control theories such as robust control, linear and non linear control, intelligent techniques (fuzzy logic and neural networks), adaptive control, sliding mode control, etc, to modern areas such as robotics, mobile robots, consensus and cooperation among multiple agents, quadrotors, and all-wheel independent drive electric vehicles. On the instrumentation front, the research interests of the group include smart and intelligent sensors, virtual instrumentation, intelligent systems and modeling, soft-computing, data mining, machine learning, brain-computer interface, computer vision, intelligent informatics, intelligent condition-based monitoring, computational intelligence, business intelligence, and related applications in various domains. The faculty members have multiple projects funded by government and private agencies, and are working on them with active support from students
On the control systems front, the research interests of the group include applications of control theories such as robust control, linear and non linear control, intelligent techniques (fuzzy logic and neural networks), adaptive control, sliding mode control, etc, to modern areas such as robotics, mobile robots, consensus and cooperation among multiple agents, quadrotors, and all-wheel independent drive electric vehicles. On the instrumentation front, the research interests of the group include smart and intelligent sensors, virtual instrumentation, intelligent systems and modeling, soft-computing, data mining, machine learning, brain-computer interface, computer vision, intelligent informatics, intelligent condition-based monitoring, computational intelligence, business intelligence, and related applications in various domains. The faculty members have multiple projects funded by government and private agencies, and are working on them with active support from students
Faculty
PG Students
Publications
Facilities
Courses
- Details
- Last Updated: Thursday, 05 October 2023 16:16
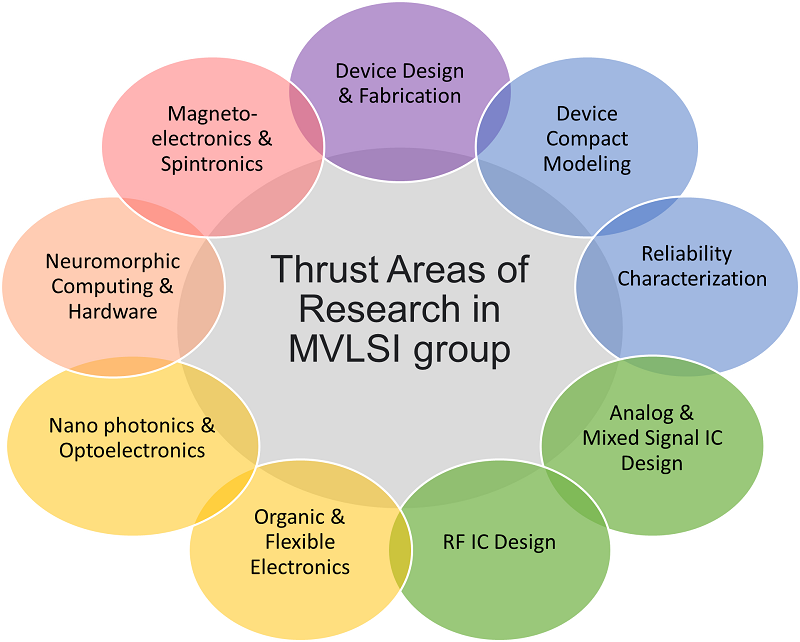
Welcome to the home of Microelectronics and VLSI stream! Our faculty members work in different areas of semiconductor research starting from device fabrication to making systems on chip.
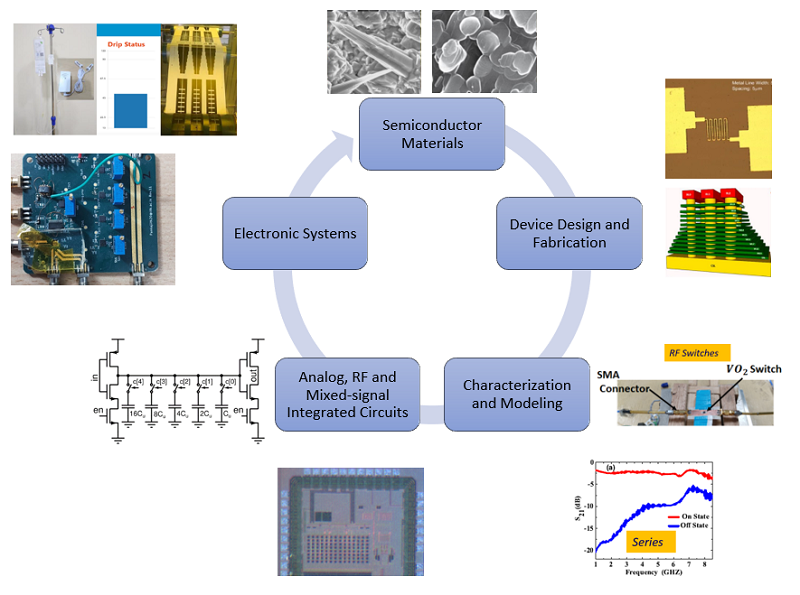
The following are some of the thrust areas of research in our group.
Faculty
PG Students
Publications
Facilities
Courses
- Details
- Last Updated: Friday, 08 December 2023 10:50
Welcome to the Signal Processing, Communications and Networking Group in the Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Kanpur. The stream offers M. Tech., dual-degree and PhD programs. The stream has always aimed at imparting technical education and equip the students with the latest technologies.
 The research interests of the faculty members include application based modern areas like Image, Video and Speech processing, Signal processing for Wireless Communication, Tomography, Biomedical Imaging, Data Mining, Computer Vision, Cooperative Spectrum Sensing, Video Compression And Decompression, Development of live lecture delivery system over Internet, Cognitive Radio, Information Theory, Scalable Video Coding based Wireless Video Transmission, Several ongoing projects are coordinated by the faculty along with active participation of the students, which are being funded by various Government and private agencies.
The research interests of the faculty members include application based modern areas like Image, Video and Speech processing, Signal processing for Wireless Communication, Tomography, Biomedical Imaging, Data Mining, Computer Vision, Cooperative Spectrum Sensing, Video Compression And Decompression, Development of live lecture delivery system over Internet, Cognitive Radio, Information Theory, Scalable Video Coding based Wireless Video Transmission, Several ongoing projects are coordinated by the faculty along with active participation of the students, which are being funded by various Government and private agencies.
Faculty
PG Students
Publications
Facilities
Courses
- Details
- Last Updated: Monday, 04 September 2023 12:39
Welcome to the Signal Processing, Communications and Networking Group in the Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Kanpur. The stream offers M.Tech., dual-degree and PhD programs. The stream has always aimed at imparting technical education and equip the students with the latest technologies.
The research interests of the faculty members include application based modern areas like Image, Video and Speech processing, Signal processing for Wireless Communication, Tomography, Biomedical Imaging, Data Mining, Computer Vision, Cooperative Spectrum Sensing, Video Compression And Decompression, Development of live lecture delivery system over Internet, Cognitive Radio, Information Theory, Scalable Video Coding based Wireless Video Transmission, Several ongoing projects are coordinated by the faculty along with active participation of the students, which are being funded by various Government and private agencies.
- Details
- Last Updated: Monday, 23 October 2023 17:10




















 Computer vision is the science and technology of machines that can see. As a scientific discipline, computer vision is concerned with the theory behind artificial systems that extract information from images. The image data can take many forms, such as video sequences, views from multiple cameras, or multi-dimensional data from a medical scanner. As a technological discipline, computer vision seeks to apply its theories and models to the construction of computer vision systems. Various reseach areas includes: Applications in Display Technology, Computer Vision for Navigation, Metrology, High Level Video Analysis, and Human Computer Interfaces. Pharmaceutical biomathematical modeling, Signal and System theory.
Computer vision is the science and technology of machines that can see. As a scientific discipline, computer vision is concerned with the theory behind artificial systems that extract information from images. The image data can take many forms, such as video sequences, views from multiple cameras, or multi-dimensional data from a medical scanner. As a technological discipline, computer vision seeks to apply its theories and models to the construction of computer vision systems. Various reseach areas includes: Applications in Display Technology, Computer Vision for Navigation, Metrology, High Level Video Analysis, and Human Computer Interfaces. Pharmaceutical biomathematical modeling, Signal and System theory.

 Faculty : Dr.R.M.Hegde
Faculty : Dr.R.M.Hegde


 Research Areas: Mobile Beacon and node localisation using array processing methods, mobile beacon tracking using signal processing methods, self-organizing autonomous sensor networks with random geometry, distributed multi sensor data fusion, situation aware multi modal sensor and cell phone networks.
Research Areas: Mobile Beacon and node localisation using array processing methods, mobile beacon tracking using signal processing methods, self-organizing autonomous sensor networks with random geometry, distributed multi sensor data fusion, situation aware multi modal sensor and cell phone networks.